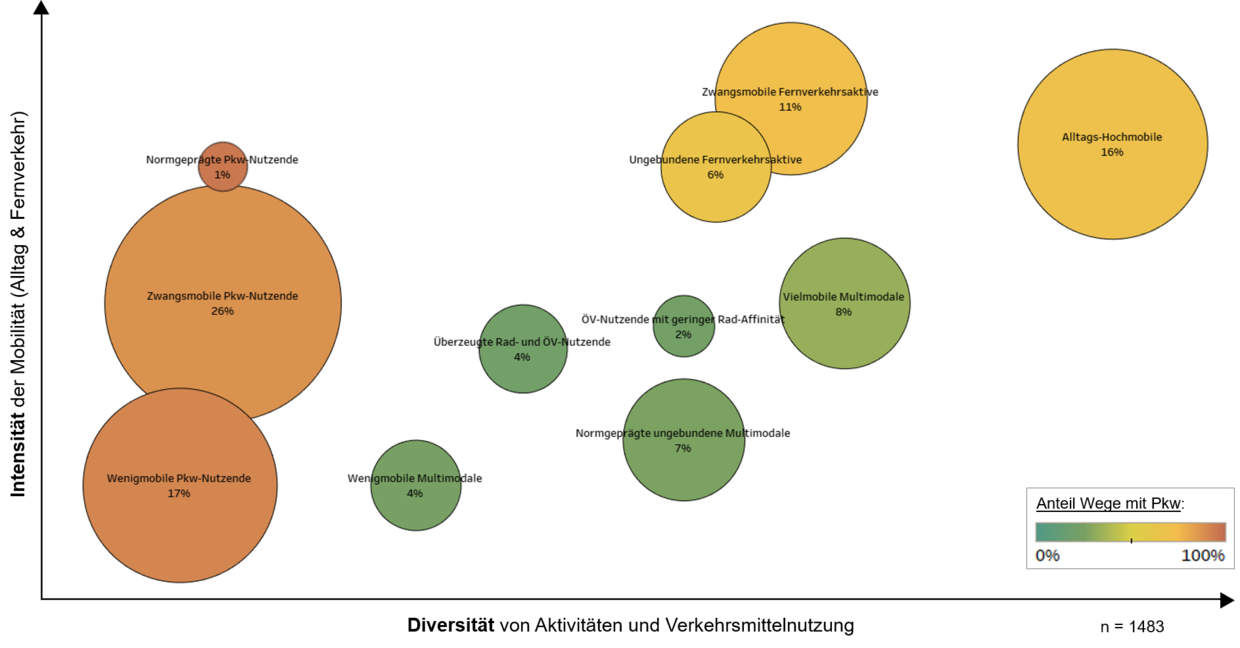
Urban Mobility Types
With the data generated through the Travel Skeleton survey, each respondent can be assigned to a specific Urban Mobility Type based on their everyday travel behavior (number of trips per day, proportion of trips by car, share of trips for everyday obligations), their long-distance travel behavior, their subjective mobility necessities, their orientation towards different means of transportation (bicycle, car, public transit), and other mobility-related attitudes. The following figure shows a qualitative visualization of the distribution of the inhabitants of the city of Los Angeles in 2023 across the eleven different Urban Mobility Types.
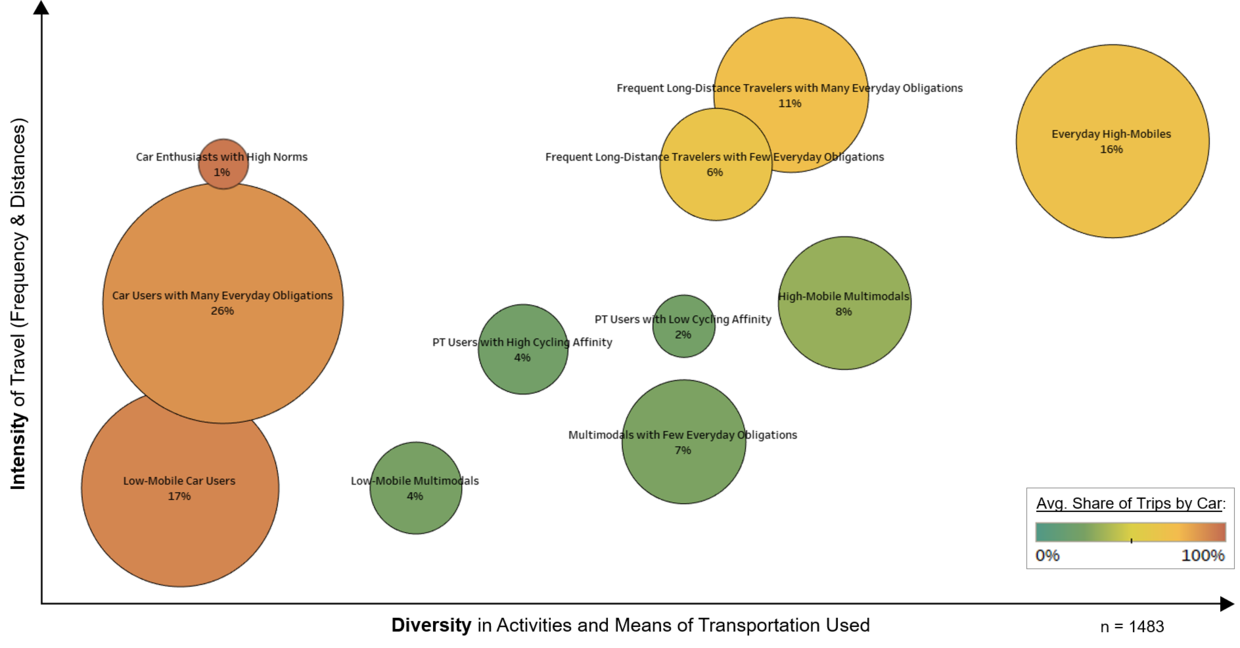
Car Dependence Types
The integrated survey of respondents' usual mobility and attitudes towards different means of transportation enables the differentiation of car dependence of car owners into two different dimensions - the objective and the subjective. This two-dimensional view of car dependence leads to the distinction of car owners into four different car dependence types, the distribution of which is visualized for the city of Los Angeles in the following figure.
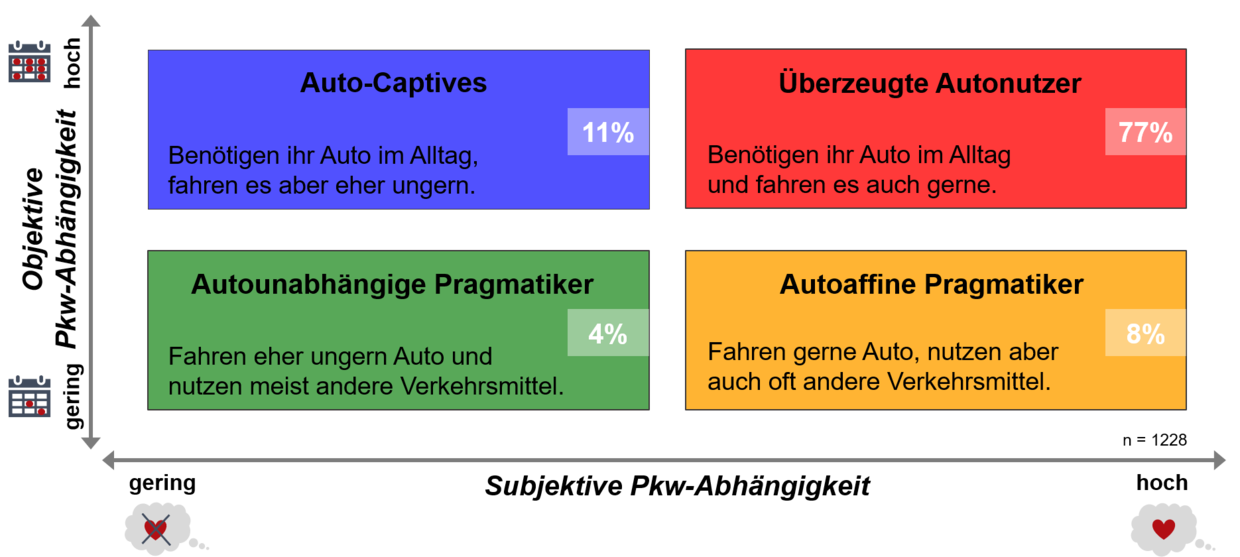
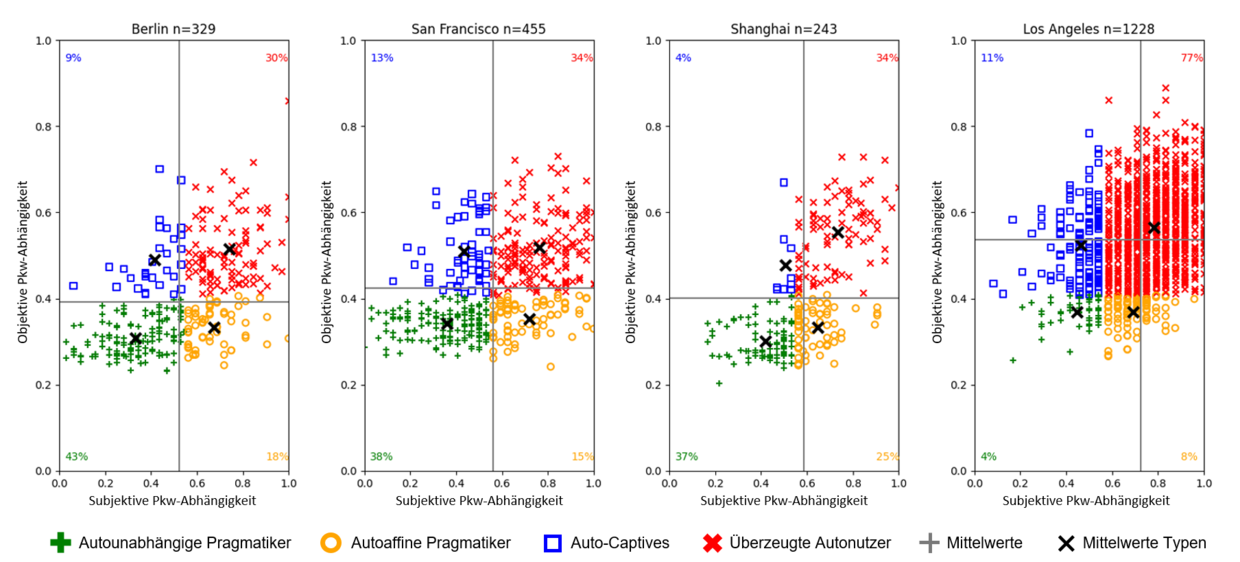
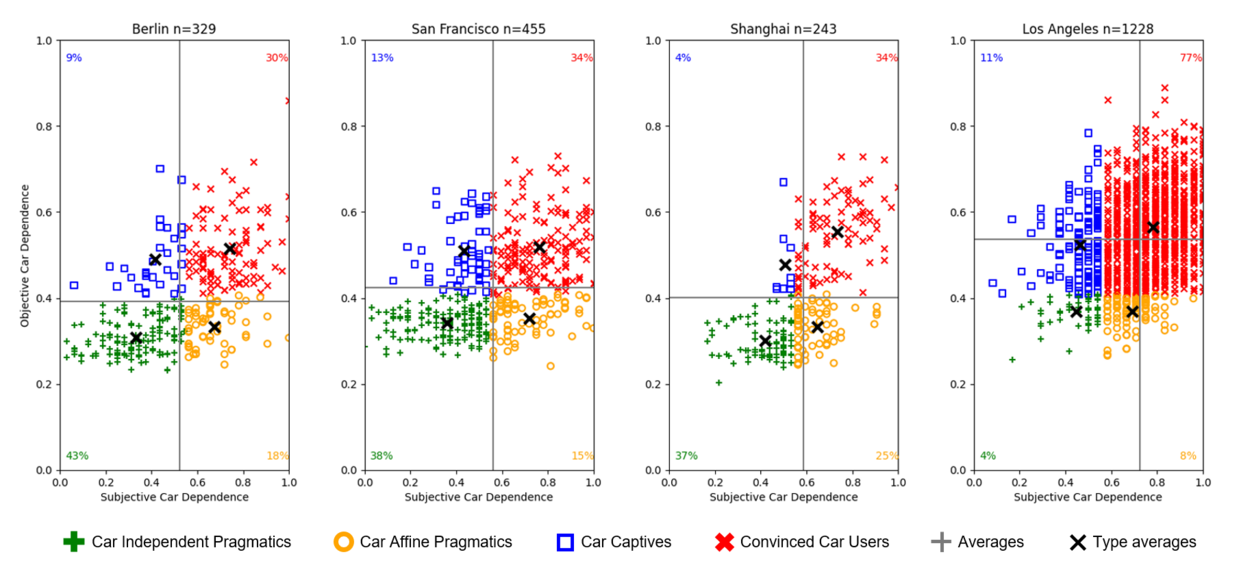
Comparison of Different Cities
Thanks to its application in several cities worldwide, the data generated through the Travel Skeleton survey can be used to compare the travel behavior and other mobility-related characteristics of the residents of these cities. For example, the figure below visualizes the objective and subjective car dependence of car owners in Berlin, San Francisco, and Shanghai (2017 in each case) as well as Los Angeles (2023). It shows that car owners in Los Angeles are significantly more car-dependent, both objectively and subjectively, than people from the other cities.